- 1 1. Introduction
- 2 2. Overview of the MySQL 9 Series and Release Background
- 3 3. Update History by Version (Summary of 9.0–9.3)
- 4 4. Highlighted New Features and Practical Use Cases
- 5 5. Comparison of New Features with Other RDBs (PostgreSQL, MariaDB, etc.)
- 6 6. Migration and Deployment Guide for MySQL 9
- 7 7. Summary and Recommended Usage Scenarios
- 8 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 8.1 Q1. Can MySQL 9.x be used in production?
- 8.2 Q2. Can the vector data type replace full-text search?
- 8.3 Q3. Is JavaScript stored procedure support available in the free Community Edition?
- 8.4 Q4. The native_password authentication method was removed—what should I do?
- 8.5 Q5. Compared to other RDBs (such as PostgreSQL or MariaDB), what are MySQL 9’s strengths?
- 8.6 Q6. What are common issues during upgrades?
- 9 9. Related Links and References
1. Introduction
MySQL is one of the most widely used relational database management systems (RDBMS) among companies and engineers worldwide. Among its versions, the “MySQL 9” series, introduced in 2024 and beyond, stands out as an “Innovation Release” that clearly differentiates itself from previous versions by incorporating numerous new features and cutting-edge technologies that further expand the possibilities of databases.
Until now, MySQL has been best known for its Long Term Support (LTS) versions such as “8.4,” which prioritize stability and robustness. However, changing technology trends and evolving market demands have increased the need for faster access to new features and early adoption of AI- and big data–driven requirements. MySQL 9 has attracted significant attention from developers and database administrators as a bold and forward-looking release designed to meet these modern demands.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of MySQL 9 (9.0–9.3), including its key features, improvements, differences from previous versions, migration considerations, and comparisons with other databases as of 2025. If you are wondering “What is MySQL 9?” or “In what scenarios is it useful?”, this guide will help you make informed decisions about database selection and system operations.
Whether you are a developer exploring the latest database technologies, an operations engineer considering an upgrade to your MySQL environment, or simply gathering technical insights, we invite you to read through to the end.
2. Overview of the MySQL 9 Series and Release Background
The MySQL 9 series represents the first wave of a new release model known as the “Innovation Release,” marking a major evolution from the MySQL 8 line. While previous upgrades focused primarily on LTS (Long Term Support) versions centered around stability, the 9 series clearly emphasizes the rapid delivery of new technologies.
The traditional LTS version, MySQL 8.4, is designed for enterprise and mission-critical systems, offering long-term guarantees for bug fixes and security patches. In contrast, the MySQL 9 Innovation Release focuses on implementing new features aligned with modern technology trends—such as AI, cloud-native development, and big data analytics—on a faster release cycle.
The background behind the MySQL 9 release lies in the rapid advancement of database technologies and the diversification of real-world requirements. For example, features such as vector search for the AI era and JavaScript stored procedures have been introduced to deliver a development experience that goes beyond traditional RDBMS capabilities. As a result, MySQL is evolving from being simply a “data storage system” into an intelligent data platform capable of performing advanced data processing and real-time analytics.
That said, Innovation Releases are best suited for developers and forward-thinking organizations that want immediate access to the latest technologies and early adoption of emerging trends. For long-term operational stability and maintainability, LTS versions (such as MySQL 8.4) remain the recommended choice. In this way, the MySQL 9 series clearly separates “innovation” and “stability,” allowing users to select the most appropriate version based on their specific needs.
In the next section, we will explore the actual feature additions and improvements introduced in MySQL 9, detailing updates by version.
3. Update History by Version (Summary of 9.0–9.3)
The MySQL 9 series is characterized by the step-by-step introduction of unprecedented new features and improvements. Here, we organize the major updates from MySQL 9.0 through 9.3, released from 2024 through spring 2025, by version.
3.1 MySQL 9.0 (Released July 2024)
MySQL 9.0 launched as the first Innovation Release. The key point of this version is that it delivers an experience that was not possible in prior releases.
Notable new features include the following.
- Introduction of a Vector Data Type
Provides native MySQL support for “vector search,” which is essential for AI and recommendation engines. - JavaScript-Based Stored Programs
Using GraalVM and ECMAScript 2023, you can write stored procedures and triggers in JavaScript (Enterprise-only feature). - JSON Output for EXPLAIN ANALYZE
Makes execution plans easier to visualize and automate, greatly improving performance-tuning efficiency. - Removal of the native_password authentication method
Shortly after release, bugs were found; MySQL 9.0.0 distribution was stopped, and the fixed MySQL 9.0.1 was promptly provided.
3.2 MySQL 9.1 (Released October 2024)
This release mainly focused on stabilizing and improving features introduced in 9.0.
- Vector type optimization and faster query performance
- Preview availability started on services such as AWS RDS
- Stronger security and permission controls
3.3 MySQL 9.2 (Released January 2025)
- Additional GIS privileges
- mysqldump enhancements (dumps that include users and privilege information)
- Introduction of EXPLAIN JSON format version 2
3.4 MySQL 9.3 (Released April 2025)
- Further vector type optimization and improved indexing
- Expanded integration APIs for operations and management tools
- Performance improvements and enhanced stability
3.5 Removed / Deprecated Features
- Complete removal of the
native_passwordauthentication method - End of support for portions of older client protocols
3.6 Future Roadmap
MySQL 9 is expected to continue adding AI-related capabilities, cloud integrations, and stronger interoperability across RDB systems. Understanding version-to-version differences and applying them based on your goals is essential.
4. Highlighted New Features and Practical Use Cases
A major hallmark of the MySQL 9 series is that it includes many innovative features that were not available in traditional RDBMS products. Here, we focus on the new features with the greatest impact in real-world environments and explain practical use cases and key considerations.
4-1. Vector Data Type
Key characteristics and what you can do
The vector data type is a new type that lets you store and search “multi-dimensional vectors” commonly used in AI and machine learning directly in the database. Previously, this often required Elasticsearch or an external vector database, but starting with MySQL 9 you can define a vector type and perform similarity search and nearest-neighbor exploration.
Example use cases
- “Find similar” searches for products or images
- Implementing recommendation systems
- Semantic search (natural-language vector search)
Sample SQL
CREATE TABLE items (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
feature VECTOR(128)
);Notes
At this time, it is not a complete replacement for full-text search, and there are some constraints around indexing and query performance.
4-2. JavaScript-Based Stored Programs
Background and key characteristics
With support for GraalVM and ECMAScript 2023, MySQL has added the ability to write stored procedures in JavaScript. This is especially attractive for web developers, as it allows them to implement database logic in a familiar language.
Sample code
CREATE PROCEDURE add_numbers(a INT, b INT)
LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT
AS
$$
return a + b;
$$;Notes
This feature is limited to MySQL Enterprise Edition and HeatWave, and it cannot be used in Community Edition.
4-3. JSON Output for EXPLAIN ANALYZE
Overview and benefits
Execution plans can now be output in JSON format, making it easier to integrate with external tools. This enables visualization and automated analysis, improving the accuracy of performance tuning.
Sample query
EXPLAIN ANALYZE FORMAT=JSON
SELECT * FROM items WHERE id = 1;4-4. Other Enhancements (GIS Privileges, mysqldump Improvements, and More)
- Introduction of GIS privileges: Enables more granular permission settings for working with geospatial data.
- mysqldump improvements: Enables complete backups including user and privilege information, making cloud migrations and environment restores easier.
MySQL 9 provides a wide range of flexible and innovative capabilities designed for the AI, cloud, and data analytics era.
5. Comparison of New Features with Other RDBs (PostgreSQL, MariaDB, etc.)
How do the advanced features introduced in the MySQL 9 series compare with other major relational database systems (RDBs)? In this section, we compare MySQL 9 with representative RDBs such as PostgreSQL and MariaDB to clarify its strengths and characteristics.
5-1. Implementation and Application of Vector Data Types
MySQL 9
- Supports a native VECTOR type, enabling similarity search and vector storage using standard SQL.
- Also supports vector distance calculations via dedicated operators (e.g., <=>).
PostgreSQL
- Vector types are not implemented in the core distribution, but extensions (such as pgvector) provide support.
- Setup and operation require a moderate level of technical expertise.
MariaDB
- No native support for vector types; alternatives typically rely on JSON types or external processing.
Summary
MySQL 9 stands out for its official, streamlined implementation, making adoption easier.
5-2. Flexibility of Stored Program Languages
MySQL 9
- Introduces JavaScript-based stored programs (GraalVM-based, Enterprise-only).
PostgreSQL
- Supports PL/pgSQL as well as multiple languages such as PL/Python, PL/Perl, and JavaScript variants.
MariaDB
- Primarily SQL-based; language options are relatively limited.
Summary
PostgreSQL leads in multi-language flexibility, while MySQL 9 focuses on accessibility for web developers.
5-3. Authentication Methods and Security Architecture
MySQL 9
- Removal of
native_password;caching_sha2_passwordis now the standard.
PostgreSQL
- Supports various security mechanisms, including SCRAM-SHA-256 and certificate-based authentication.
MariaDB
- Similar to MySQL, but tends to maintain support for legacy authentication methods.
Summary
MySQL 9 is progressive in standardizing security defaults, while PostgreSQL provides more granular control.

5-4. Backup and Operational Tooling
MySQL 9
- Enhanced
mysqldump(supports dumps including users and privilege information).
PostgreSQL
- Comprehensive tooling such as pg_dump and pg_basebackup; supports snapshot-based operations.
MariaDB
- Inherits similar tools from MySQL, though feature additions are more conservative.
Summary
MySQL 9 achieves a high standard for cloud readiness and full backup capability.
5-5. Future Development and Technical Roadmap
MySQL 9 is characterized by the rapid official delivery of new features. PostgreSQL emphasizes open-source extensibility, while MariaDB balances compatibility with independent innovation.
Each database has distinct strengths, so selecting the right one depends on your project requirements and development strategy.
6. Migration and Deployment Guide for MySQL 9
Because MySQL 9 actively incorporates new technologies, migrating from existing environments or deploying it in new systems requires careful planning. This section outlines practical checklists, compatibility considerations, cloud deployment guidance, and trial rollout steps.
6-1. Checklist for Existing Environments
Verify authentication methods
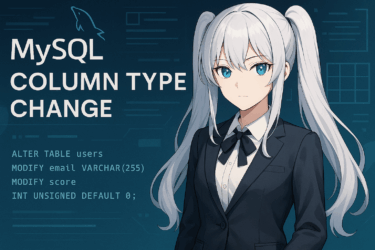
In MySQL 9, native_password authentication has been removed, and newer methods such as caching_sha2_password are now standard. Before upgrading from older versions, verify that your applications and client tools support the updated authentication method.
Client and driver compatibility
Confirm that MySQL drivers for PHP, Python, Java, and other environments officially support MySQL 9. Some driver versions may cause connection errors or unexpected behavior.
6-2. Compatibility and Migration Considerations
Handling removed features
Certain APIs, authentication methods, and configuration parameters from older versions have been removed or deprecated. Review the official deprecation and removal list before migration.
SQL syntax and data type review
With the addition of new features, SQL syntax and data type behavior may have changed. Thorough pre-migration testing is essential, especially for custom SQL implementations or legacy systems.
6-3. Cloud Deployment (AWS RDS, Google Cloud, etc.)
Version availability
Support for MySQL 9 is expanding across services such as AWS RDS and Google Cloud SQL. Always verify availability, version restrictions, and service-specific conditions.
Cloud migration considerations
- Permission management and network configuration may be subject to cloud-provider constraints.
- Combining cloud-native backup/restore features with MySQL 9 tools such as
mysqldumpimproves reliability and safety.
6-4. Trial Deployment Workflow (Simplified)
Step 1: Backup and environment assessment
Before migration, perform a full backup and document your current version, configuration settings, and user privileges.
Step 2: Validate in a test environment
Do not apply changes directly to production. Instead, deploy MySQL 9 on a test server or via Docker and reproduce migration scenarios.
Step 3: Compatibility checks and tuning
Evaluate the impact of deprecated and new features, and adjust SQL or applications as needed.
Step 4: Production migration and monitoring
During the initial production phase, continuously monitor logs and performance metrics and ensure rapid response capabilities.
6-5. Choosing Between LTS (8.4) and Innovation (9 Series)
- LTS (8.4): Ideal for business-critical systems requiring stable, long-term operation.
- Innovation (9 Series): Best suited for development teams adopting AI capabilities and emerging technologies early.
The MySQL 9 series offers flexibility to meet a wide range of needs.
7. Summary and Recommended Usage Scenarios
The MySQL 9 series distinguishes itself from traditional LTS versions as a forward-looking, innovation-driven database that brings transformation to modern environments. In this chapter, we summarize which types of users and environments are best suited for the 9 series and provide clear criteria for choosing between MySQL 9 and LTS (8.4).
7-1. Who Should Consider MySQL 9?
- Services actively leveraging AI and machine learning
- New web development or SaaS launch projects
- Teams heavily utilizing cloud environments and seeking rapid database innovation
- Development teams aiming to differentiate by adopting emerging technology trends early
7-2. When to Choose LTS (8.4)
- Systems where long-term operational stability is the highest priority
- Legacy environments emphasizing compatibility and extended support
- Large organizations where frequent version upgrades are difficult to manage
7-3. Example Decision Flow
- Is this a new development project or an upgrade to an existing system?
- Are AI capabilities or vector search required?
- Will Enterprise-only features such as JavaScript stored programs be used?
- Does your team have the operational capacity to handle frequent upgrades?
7-4. Future Outlook and Key Watch Points
The MySQL 9 series is expected to continue receiving regular feature updates. AI-related functionality, advanced analytics capabilities, cloud integrations, and further performance improvements are areas to watch closely.
The value of MySQL 9 depends on what your organization prioritizes today. Clearly defining when to use LTS versus Innovation releases enables the most strategic and optimal database selection.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
There are many common questions regarding differences from previous versions and the latest capabilities of the MySQL 9 series. Below are frequently asked questions from real-world environments and their answers.
Q1. Can MySQL 9.x be used in production?
A.
MySQL 9.x is an Innovation Release, designed for environments that prioritize flexibility and access to new features. Production use is possible, but your team must be prepared to handle upgrades and potential troubleshooting. If maximum stability is required, the LTS version (such as MySQL 8.4) is recommended.
Q2. Can the vector data type replace full-text search?
A.
The vector data type is designed for similarity-based searches (“semantic closeness”) and differs from traditional full-text search based on exact string matching. It is best used as a complementary feature rather than a replacement.
Q3. Is JavaScript stored procedure support available in the free Community Edition?
A.
Currently, JavaScript stored programs are available only in MySQL Enterprise Edition and HeatWave. They are not supported in Community Edition.
Q4. The native_password authentication method was removed—what should I do?
A.
MySQL 9 recommends caching_sha2_password and other secure authentication methods. Before migration, verify that your applications and connection libraries support the new authentication method and update configuration settings accordingly.
Q5. Compared to other RDBs (such as PostgreSQL or MariaDB), what are MySQL 9’s strengths?
A.
MySQL 9 provides rapid official support for new capabilities such as the vector data type and JavaScript stored programs. It is particularly strong in web development scenarios and cloud integration use cases.
Q6. What are common issues during upgrades?
A.
Common issues include authentication method changes, removal of deprecated features, and SQL syntax differences. Always perform thorough testing in a staging environment and ensure full backups before upgrading.
9. Related Links and References
If you want to explore MySQL 9 in greater depth, using official documentation, expert blogs, and community resources is highly effective. Below are trusted references and useful links.
9-1. Official Documentation and Release Notes
9-2. Technical Articles and Case Studies
- MySQL Blog (Official Development Team Updates)
- Developer community platforms such as Qiita and Zenn (search for “MySQL 9 new features”)
9-3. Community and Forums
9-4. Other RDB Official Sites
9-5. How to Stay Updated
Because release notes and official blogs are updated regularly, checking them frequently ensures you stay current. When evaluating or operating MySQL 9, leverage the resources introduced here to build more robust and future-ready systems.