- 1 1. Investment Risks in the South African Rand and What “Explosion-Loss” Means
- 2 2. Fundamental Overview of the South African Rand
- 3 3. Causes Triggering an “Explosion-Loss”
- 4 4. Real-world “Explosion-Loss” Cases
- 5 5. Risk-Avoidance Measures Investors Should Take
- 6 6. Outlook for the South African Rand
- 7 7. Key Points for Smart Investing
- 8 References
1. Investment Risks in the South African Rand and What “Explosion-Loss” Means
Risks Lurking in South African Rand Investments
The South African Rand (ZAR) is a currency many investors focus on—primarily because of its high interest yield. With large swap-point opportunities versus the Japanese yen, it is known among FX investors as a currency that can offer attractive returns. However, among investors you will often hear the term “South African Rand explosion-loss.” This refers to cases where the Rand suddenly loses value and results in significant losses.
Especially as an emerging-market currency, the South African Rand exhibits higher volatility compared to major developed-market currencies, and is sensitive to external factors. It tends to be influenced heavily by commodity prices and political/economic changes, meaning that its fluctuation range is often larger than other currencies—so there is a risk of suffering large losses overnight.
What Drives an “Explosion-Loss”?
“Explosion-loss” literally means incurring a large loss. In the context of South African Rand investment, the main causes that push investors toward such an outcome include:
- Sudden collapse in commodity prices
- Political instability or domestic economic collapse
- Rapid depreciation of the Rand versus major currencies such as the US dollar or Japanese yen
In this article we will explain these risk factors in detail and present key points so that readers can avoid “explosion-loss” when investing in the South African Rand.

2. Fundamental Overview of the South African Rand
What is the South African Rand (ZAR)?
The South African Rand (ZAR) is the currency of the Republic of South Africa, and a representative emerging-market currency. This currency is known in international FX markets as a high-interest currency, and has drawn attention in particular for long-term investments aimed at swap points. Because the Rand’s economy is strongly dependent on mineral resources, commodity price movements have a major impact on its value.
The South African Rand is historically one of the currencies with very volatile value; notably, during the resource-price boom in the 2000s its value rose rapidly. However, during global economic crises such as the Lehman Shock and the COVID-19 shock, it experienced sharp declines, and many investors incurred losses as a result.
The Attraction and Risks of High Interest Rates
The reason the South African Rand is attractive to investors is that its policy interest rate is very high. As of September 2024, South Africa’s policy interest rate stood at 8.25%—a very high level compared to major developed countries. Meanwhile, Japan’s policy interest rate is extremely low at 0.25%, generating a large interest-rate differential between the Rand and the yen. Many investors utilize this differential via swap-point trades to aim for stable long-term returns.
However, this high-interest currency comes with substantial risk. Emerging-market currencies in particular carry risks due to political instability and fragile economic structures, making large currency value fluctuations likely. For example, issues such as domestic power-supply problems in South Africa, high unemployment, and fluctuations in mineral-resource prices strongly impact the Rand’s value. Also, because the Rand responds sensitively to global financial-market changes and movements of the US dollar, short-term risk is significant.
Volatility of the South African Rand
Like other emerging-market currencies, the South African Rand is very volatile. In concrete terms, it is prone to large price fluctuations over short periods, and during the Lehman Shock or COVID-19 shock it recorded significant short-term declines. This is due to underlying factors such as South Africa’s political instability and economic problems.
When dealing with a high-volatility currency, proper risk-management is extremely important. It is critical to perform funds-management that can withstand short-term price swings, and for long-term investment, to use swap-point strategies to accumulate profit.

3. Causes Triggering an “Explosion-Loss”
1. Domestic Economic Problems in South Africa
A major cause of the South African Rand suffering an “explosion-loss” is domestic economic instability. In particular, the national power provider, Eskom, faces serious operational issues. Eskom handles approximately 90% of the country’s electricity supply, but due to long-term mismanagement and corruption it has been brought near collapse. As a result, frequent rolling blackouts occur and have negative effects on all economic activities.
Furthermore, South Africa grapples with a severe unemployment problem—especially among the youth, where the unemployment rate exceeds 60%. High unemployment hinders economic growth and negatively impacts the Rand’s value. Additionally, South Africa’s economy depends heavily on mineral resources, so weak commodity-prices or mining-operational issues can cause the Rand’s value to decline sharply.
2. Impact of the Global Economy
The South African Rand is also a currency that is highly affected by the global economy. Especially since South Africa has strong economic ties with China, a slowdown in the Chinese economy directly affects the Rand’s price. For instance, in periods of US-China trade friction or Chinese-economic deceleration, the South African Rand tends to be sold off heavily.
In addition, global financial-market trends and the strength of the US dollar greatly impact the Rand. For example, if the United States raises interest rates, investors tend to avoid risk assets and sell emerging-market currencies while moving assets into the US dollar. This can cause the Rand’s value to fall rapidly.
3. Fluctuations in Commodity Prices
South Africa is a country rich in mineral resources, and especially the prices of gold and platinum have a major influence on the Rand. In past examples, when commodity prices surged, the Rand’s value also climbed rapidly; conversely, when commodity prices fell, the Rand’s value plummeted sharply. During the COVID-19 shock in 2020, global commodity prices remained weak, and the South African Rand experienced a rapid decline.
As such, the South African Rand is highly dependent on domestic and international economic conditions, political factors, and commodity prices—making it prone to rapid and large value swings. This is a major cause of the “explosion-loss”.
4. Real-world “Explosion-Loss” Cases
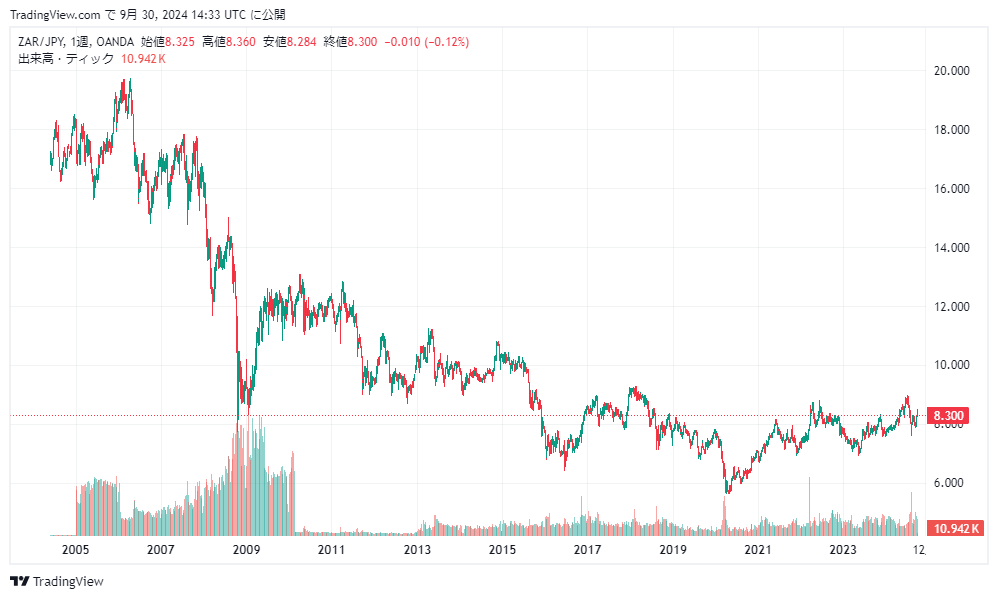
1. Large Decline of the South African Rand during the Lehman Shock
The 2008 Lehman Shock dealt a severe blow to the global economy—and the South African Rand was no exception. Prior to the Lehman Shock, South Africa had benefited from rising commodity prices and the Rand’s value was on the upswing. But once the financial crisis hit, risk-avoidance behavior intensified and investors sold off emerging-market currencies, shifting assets into safer currencies such as the US dollar and Japanese yen.
As a result, the South African Rand fell dramatically in a short period and many investors found themselves in an “explosion-loss” state. Investors who had concentrated their positions in the Rand without diversification incurred large losses. The Lehman Shock highlighted the high volatility of the Rand and the risks of emerging-market currencies.
2. Sudden Drop during the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 also had a large impact on the South African Rand. In the early phase of the pandemic, global economic activity stalled and commodity prices plunged, which in turn triggered a large decline in the Rand’s value. In particular, South Africa’s domestic economy was deeply affected by COVID-19, with mining operations halted and economic activity severely disrupted.
Moreover, the global uncertainty drove the sell-off of risk assets and the Rand was sold off heavily compared to safe currencies like the yen or the US dollar. This pandemic-triggered impact again demonstrated that the “explosion-loss” risk of the South African Rand is influenced strongly by the international economic environment.
3. US–China Trade Friction and the South African Rand
The US–China trade friction that has persisted since 2018 also significantly affected the South African Rand’s price. South Africa holds strong economic ties with China, especially for mineral-resource exports. When the US–China trade war slowed China’s economy, the South African Rand too was impacted and its price dropped substantially.
As a result, short-term investors suffered large losses and found their investment assets rapidly diminished—an “explosion-loss” scenario. This again underscored that concentrated investment in the Rand is a risk.
5. Risk-Avoidance Measures Investors Should Take
1. The Importance of Diversification
The South African Rand is a highly volatile currency, and to handle abrupt price changes it is important to diversify appropriately. The foundation of diversification is not to concentrate investments solely in the South African Rand, but to allocate across other currencies and assets. For example, by investing also in stable currencies like the yen or US dollar, or across asset classes such as stocks, bonds, or real estate—with differing risk profiles—you can mitigate the risk posed by sudden Rand declines.
Especially because emerging-market currencies carry higher risk compared to developed-market currencies, when investing in the South African Rand it is recommended to also hold other safe assets to suppress risk. Additionally, during times of global economic instability, it is crucial to reassess your overall portfolio and act flexibly in order to reduce risk.
2. A Long-Term Strategy Using Swap Points
Since the South African Rand is a high-interest currency, a long-term investment strategy utilizing swap points is effective. Swap points refer to the profit derived from the interest-rate differential in trades between currencies. Because there is a large interest-rate gap between the South African Rand and the Japanese yen, you can earn daily swap points by holding the currency pair long-term.
However, even when aiming for swap-point profits the risk-management is essential. If the Rand’s value drops precipitously, you may incur exchange-rate losses that exceed your swap-point gains. Therefore, when holding a long-term position you need funds-management that anticipates currency-risk. Also, regularly checking economic conditions in South Africa and monitoring policy-interest-rate trends, then adjusting your position as needed, leads to risk-avoidance.
3. Utilizing Automated Trading Systems
In FX trading, one method to manage risk automatically is to use automated trading systems. Especially for a highly volatile currency like the South African Rand, systems that trade based on pre-set conditions can be helpful. This enables the investor, even if they cannot respond immediately to sudden market shifts, to minimize losses according to the rules established in advance.

6. Outlook for the South African Rand
1. Economic Outlook and Expert Opinions
The outlook for the South African Rand involves multiple intertwined factors. In particular, economic instability within South Africa and external factors are at play. Although South Africa’s policy interest rate remains at a high level, issues such as domestic unemployment and energy-supply problems persist, so the growth outlook is far from optimistic. For example, the GDP growth rate in 2024 is projected to be only around 0.6% to 1.2%—this is because domestic and external headwinds are constraining growth.
Also, the South African Rand is deeply linked to China’s economy, and going forward it may continue to be significantly influenced by China’s economic condition. China is a major trade partner, and since mineral-resource exports account for a large portion of South Africa’s economy, a slowdown in China may trigger a Rand decline.
Major financial institutions such as Standard Bank assume that the policy interest rate will remain unchanged when forecasting future Rand trends; however, unless the energy issues or unemployment improve, they view any Rand upside as likely limited.
2. AI-Based Rand Market Forecasts
Forecasts using AI for future Rand exchange-rates are also gaining attention. According to AI forecasts, the trading range between the South African Rand and Japanese yen in 2024 is estimated at approximately ¥6.5 to ¥8.5. AI takes into account factors such as risk sentiment in financial markets, changes in the global financial environment, commodity-price trends, and South Africa’s policy interest rates.
However, AI forecasts should only be used as one reference among many; actual market movements may differ. While AI forecasting accuracy has improved, especially unpredictable factors such as political instability or natural disasters remain difficult to model—and human insight still plays a vital role, so one should use these predictions cautiously.
3. Long-Term Prospects for the South African Rand
In the long term, structural reforms in South Africa are indispensable for stabilizing the Rand. Domestic challenges such as improving energy supply and reducing unemployment are currently being addressed, but no immediate solution has been found. And as long as global commodity-price fluctuations continue, the value of the South African Rand may continue to show large volatility.
Therefore, for investors it is important to adopt a long-term perspective and risk-management that is not swayed by short-term price fluctuations. Investing in the South African Rand requires cautious risk evaluation and proper diversification of investments.

7. Key Points for Smart Investing
How to Avoid “Explosion-Loss” in South African Rand Investments
Investing in the South African Rand is attractive for its high interest yield via swap points, but because of its very high volatility, the risks are also significant. Learning from the “explosion-loss” cases and risk factors introduced in this article, you can implement the following points to invest wisely.
1. The Importance of Diversification
Concentrating investment only in the South African Rand is very dangerous. Aim to diversify your investment portfolio and allocate also into stable developed-market currencies and other asset classes. This increases your resilience against a sudden collapse of the Rand.
2. Long-Term Investing Utilizing Swap Points
The swap-point feature of the South African Rand is a powerful tool for long-term profits. However, rather than relying solely on swap-point profits, it is essential to manage currency risk properly. Ensure your funds-management can absorb price shocks, and adopt a strategy that reduces risk.
3. Stay Sensitive to Global Economy and Commodity-Price Trends
The South African Rand is strongly influenced by commodity price movements and global economic trends. Pay attention to China’s economic condition, global interest-rate policy, trade frictions and other factors, and make appropriate trade decisions at appropriate timing. Also, regularly check market conditions and manage the period during which you hold the Rand.
4. Thorough Risk Management and Use of Automated Trading
Because this currency is highly volatile, risk-management is extremely important. In FX trading in particular, using automated trading systems that can respond swiftly to sudden market changes is advantageous. Automated trading systems operate without emotional bias, making them especially suitable for beginner investors.
South African Rand Investing: High Risk, High Reward
Investments in the South African Rand, with proper risk-management and strategy, can aim for stable income via swap points. However, never forget the high price-fluctuation risk, and proceed with caution from a long-term perspective. While you cannot avoid risk altogether, taking appropriate measures allows you to sidestep an “explosion-loss” and aim for sound asset-management.
References
「通貨の特徴と選び方 (南アフリカランド) 」ページです。外貨預金のお預入れに当たっては、各通貨の特徴や傾向を理解するこ…










